
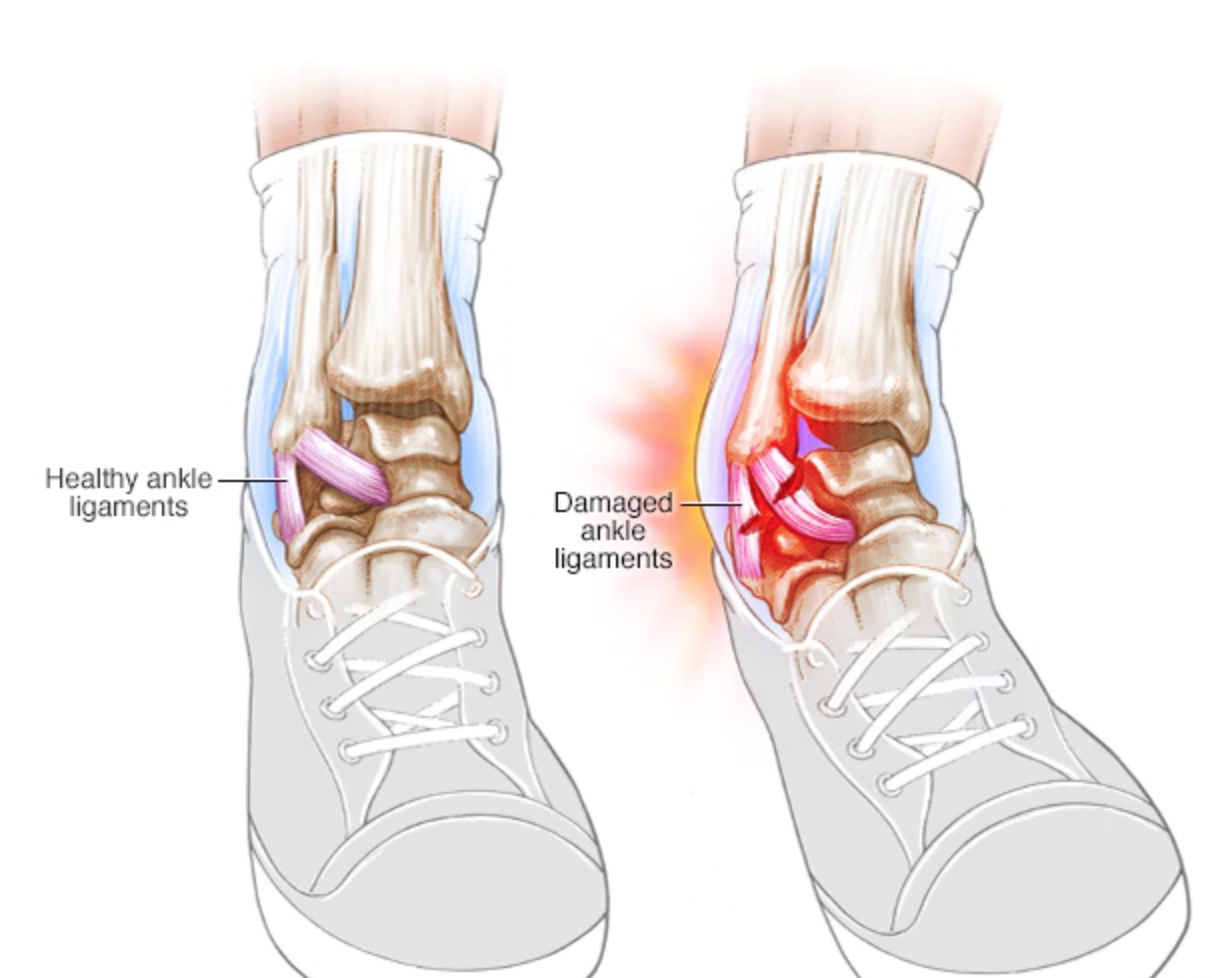
The anterior talofibular ligament courses obliquely, posterolaterally to anteromedially with respect to the tibiotalar joint, which allows resistance of internal rotation of the talus and not just anterior translation. In these situations, because of the advantage of noninvasiveness and superior soft-tissue imaging capabilities, MRI may be a useful diagnostic modality to delineate intraarticular or extraarticular sources of ankle pain after a sprain that might not have been apparent clinically. Although most ankle sprains are treated conservatively with functional rehabilitation or an Aircast or Air-Stirrup ankle brace (DJO) for persistent or residual ankle disability, surgical approaches, such as reapproximation of the torn ligament or reconstruction of the ligament repair may be considered as treatment options. According to biomechanical studies, the anterior talofibular ligament is the weakest lateral ankle ligament, followed by the calcaneofibular ligament. The anterior talofibular ligament is the most commonly injured ligament in ankle inversion injuries. Keywords: arthroscopy, ligament injury, MRI A cortical defect with bright dotlike or curvilinear high-signal-intensity lesions on T2-weighted MRI may be an additional morphologic feature to increase the diagnostic performance of detecting anterior talofibular ligament injuries, including those with partial tears. The interobserver agreement rate for the presence of anterior talofibular ligament disruption using criterion 1, both criteria, and the bright rim sign was fair to excellent.ĬONCLUSION. By adding criterion 2 to the diagnosis, the sensitivity for anterior talofibular ligament injury was increased significantly ( p < 0.01), and 8–12 additional patients with anterior talofibular ligament injury were diagnosed, most of whom exhibited a partial tear of the anterior talofibular ligament on arthroscopy. When the MRI diagnosis was based on both criteria 1 and 2, anterior talofibular ligament disruption was diagnosed with a sensitivity of 90.9–97.0% and an accuracy of 88.2–94.1%. When the MRI diagnosis was based on criterion 1, anterior talofibular ligament disruption was diagnosed with a sensitivity of 60.6–66.7% and an accuracy of 58.8–67.6%. Arthroscopy showed anterior talofibular ligament disruption in 33 patients. After MRI, ankle arthroscopy was performed in all patients for a definitive diagnosis.

If MRI revealed nonvisualization of the ligament, ligament discontinuity, and unusual ligament thickening (criterion 1) or the bright rim sign (criterion 2), the injury was considered to be a ligament disruption. All patients underwent 3-T MRI for the diagnosis of anterior talofibular ligament injury. The study included 34 patients who had an ankle injury and underwent arthroscopic surgery.

The purpose of this article is to determine whether bright rim lesions on MRI are a marker for anterior talofibular ligament injury.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
